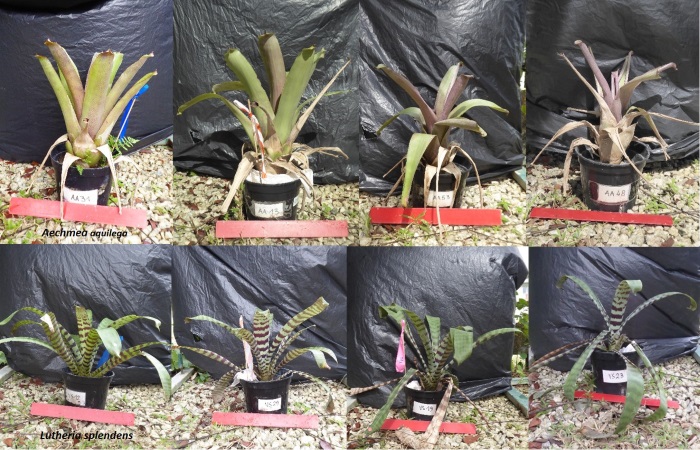
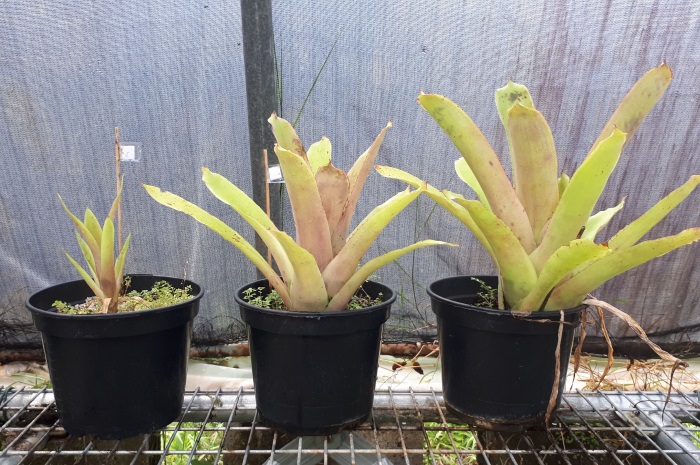
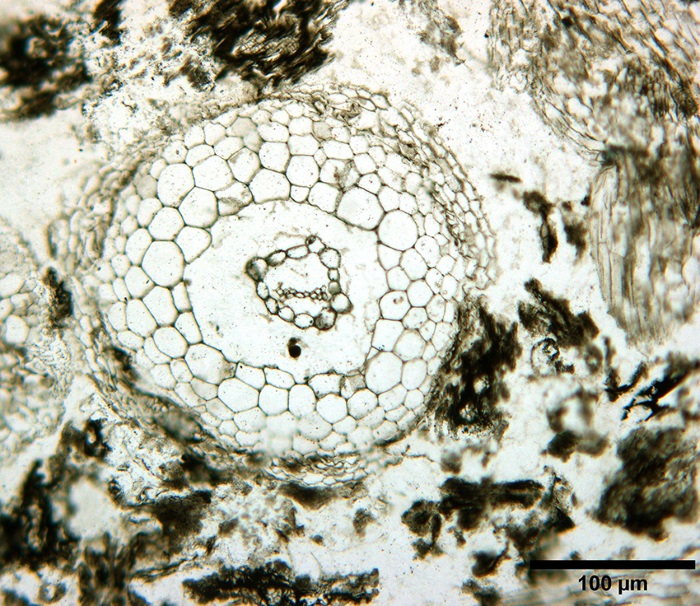
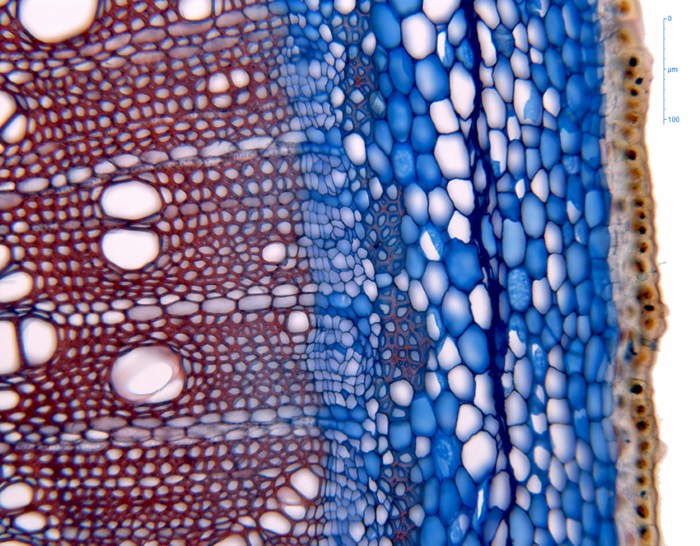
DISTEC - DISturbance ECology in a changing World
Keywords
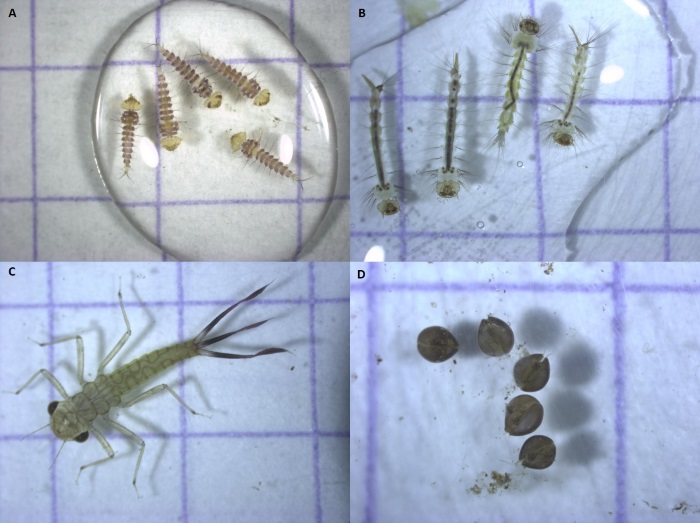
This theme encompasses the study of disturbances, their ecological impacts, and the complex interactions between natural and anthropogenic drivers of change. It aims to understand how ecosystems respond, adapt, and recover from disturbances, and how to manage and conserve them in the face of ongoing global change.
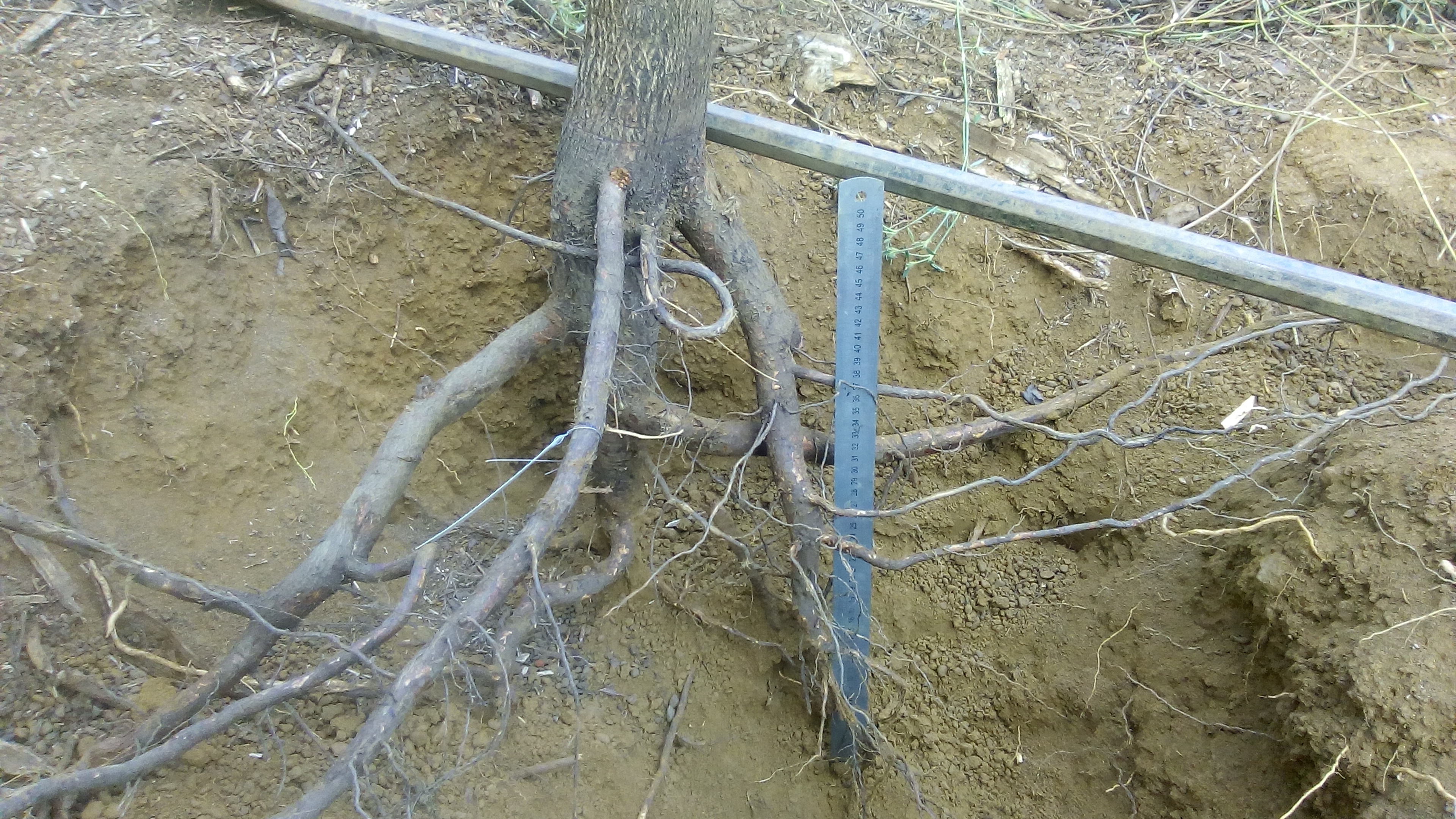
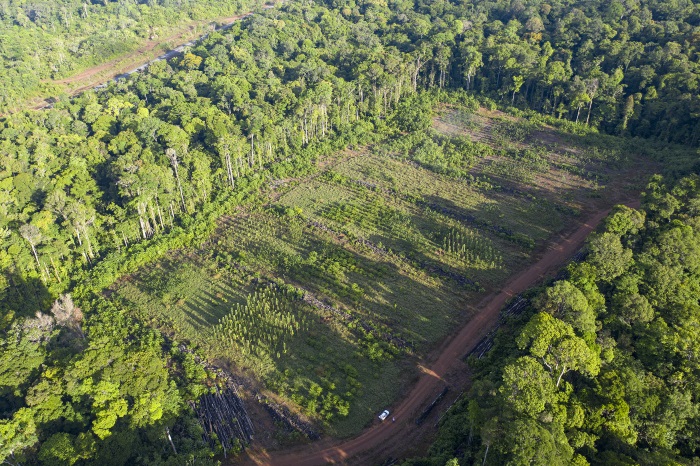
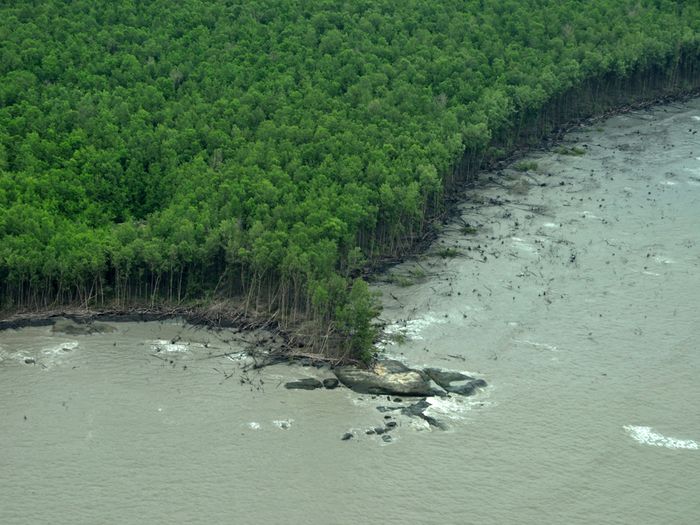
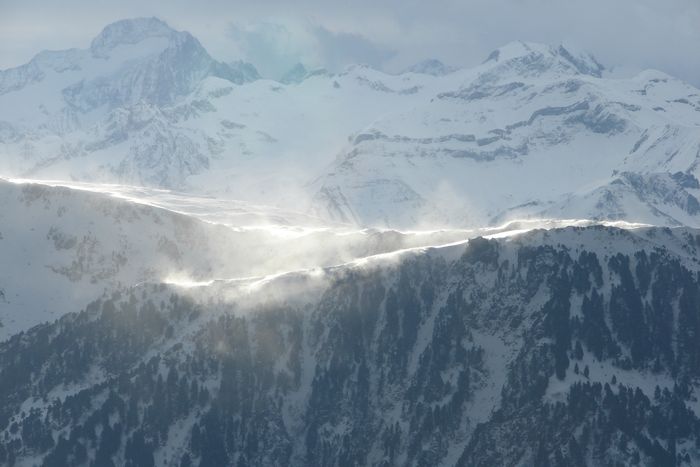
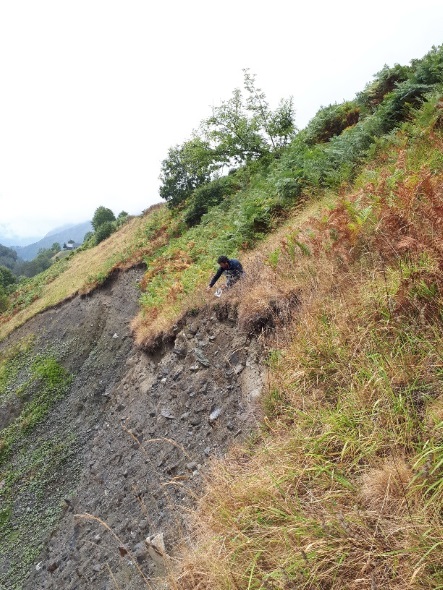
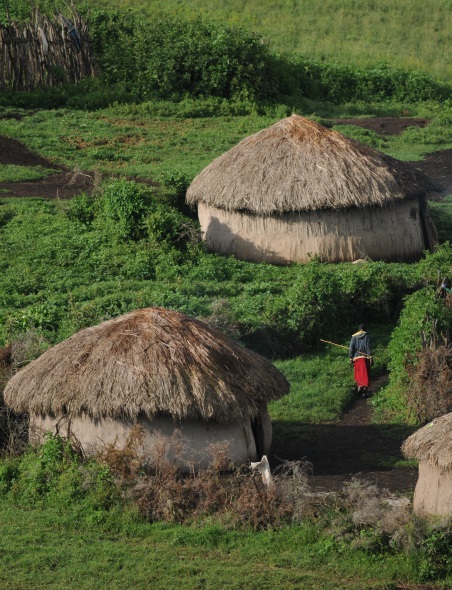
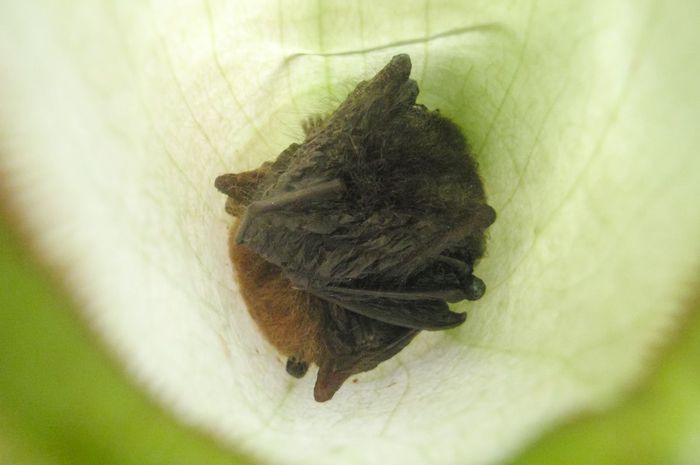
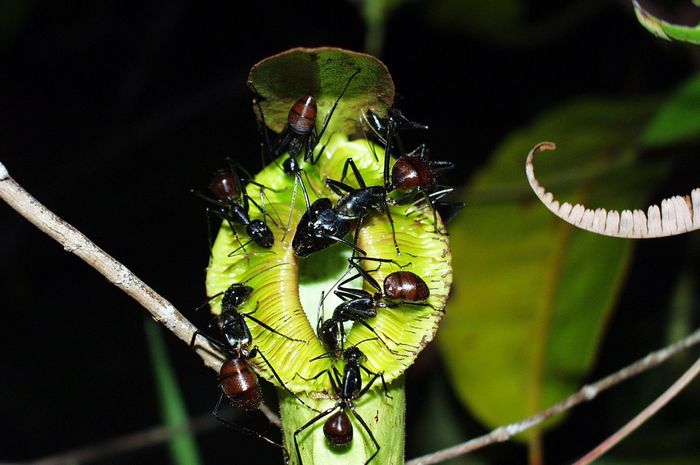
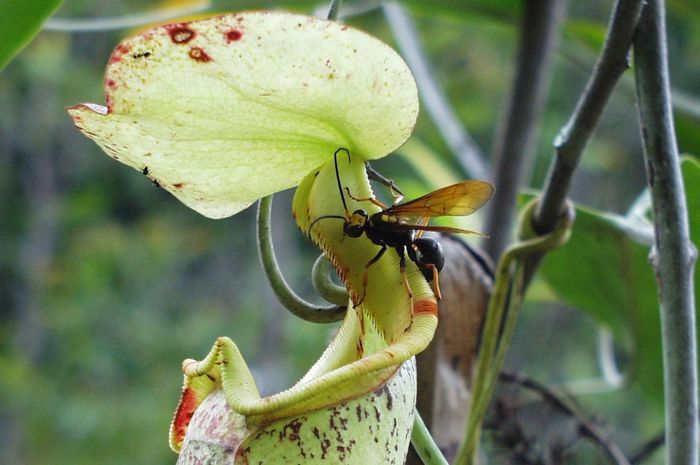
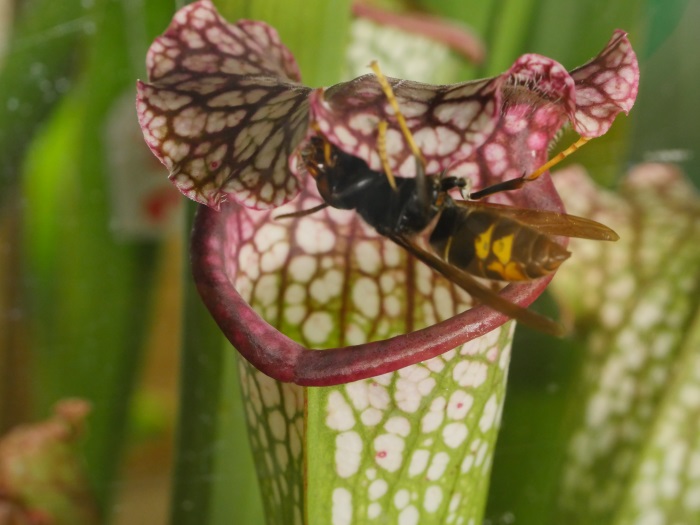
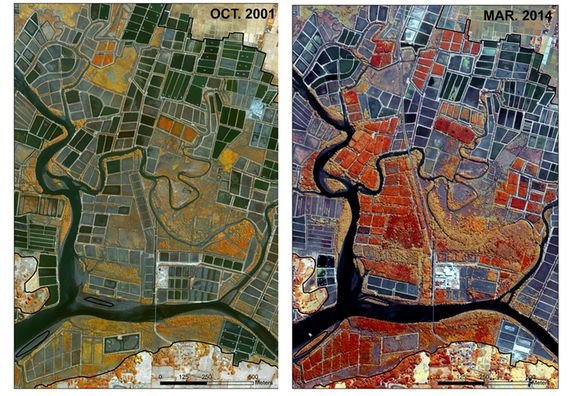
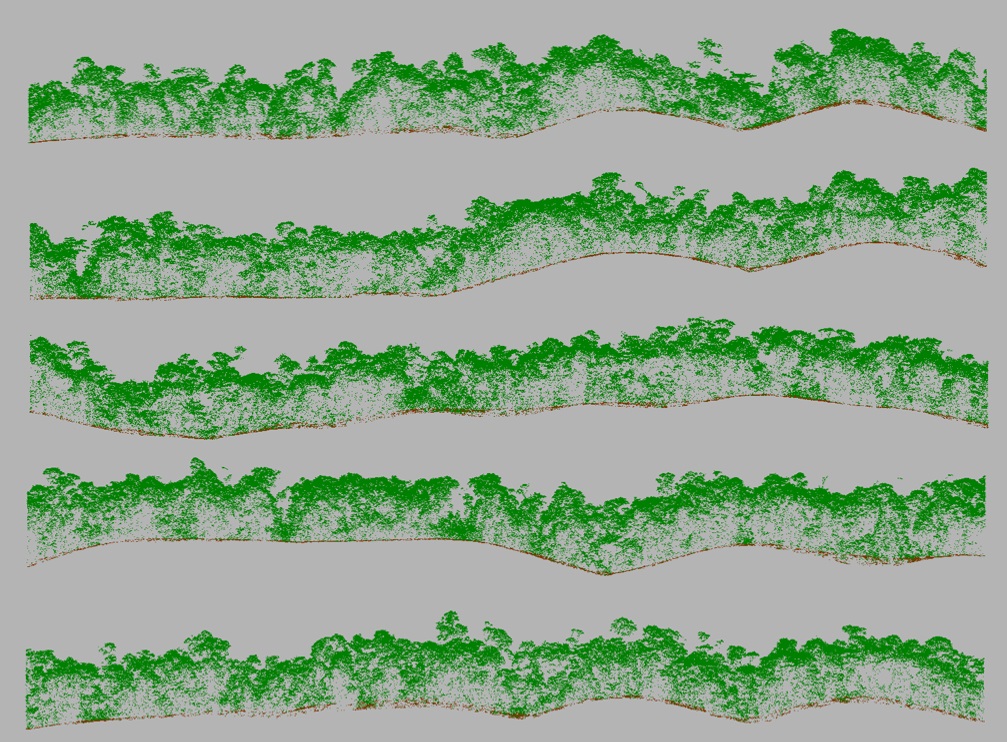
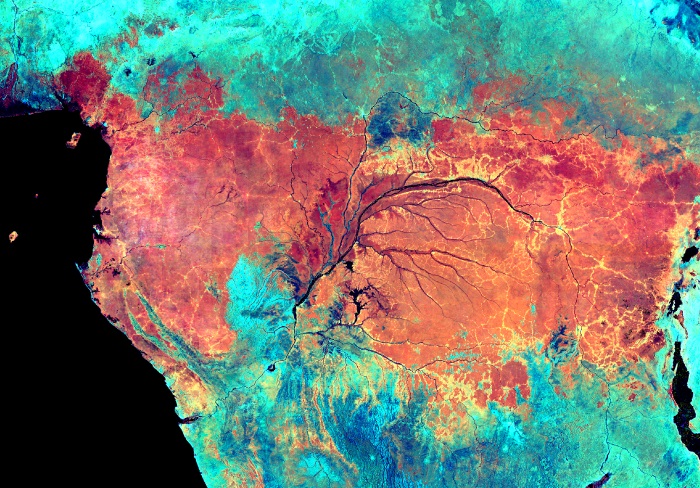
"With the accumulating evidence of changing disturbance regimes becoming increasingly obvious, there is potential for disturbance ecology to become the most valuable lens through which climate-related disturbance events are interpreted" (Newman 2019). The world biodiversity is currently exposed to unprecedented changes in disturbance regimes. Human activities have not only changed the frequency and intensity of disturbances but also changed the environmental conditions in which biodiversity have to face these disturbances. Furthermore, biodiversity is increasingly facing multiples, potentially interacting, disturbances and stresses that can cause cascading effects and dramatic changes in the structure and composition of the vegetation. These novel climate and disturbance regimes are both heavily modified by human activities and affecting natural ecosystems and human societies. Living in a changing world calls for addressing several challenging questions such as: how to identify disturbance-prone versus -averse vegetation types and biodiversity? How do organisms and ecosystems cope with regular vs. exceptional disturbances? How to restore ecosystems after heavy disturbances? How to reconcile human activities and historical disturbance regimes? How is climate change shifting the rules?
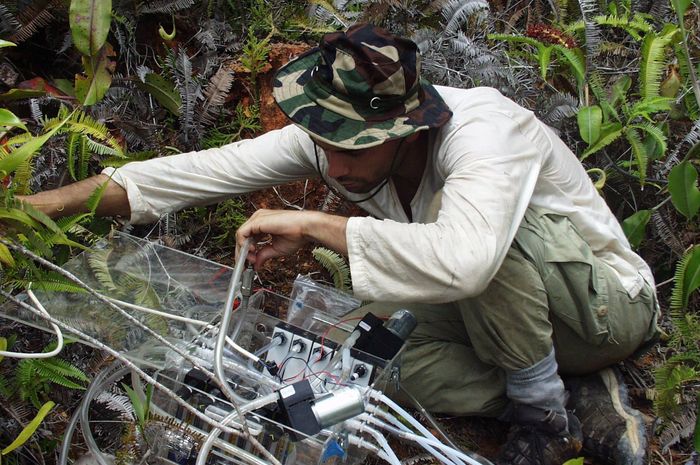
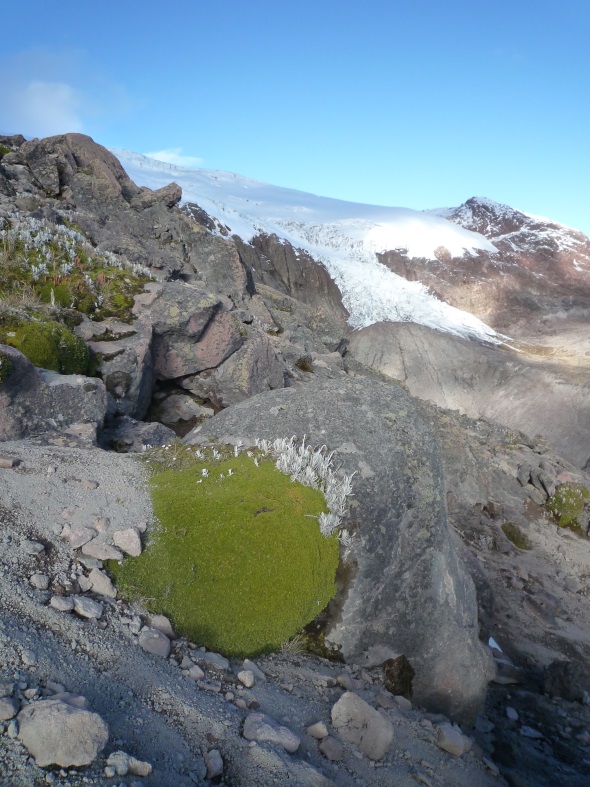
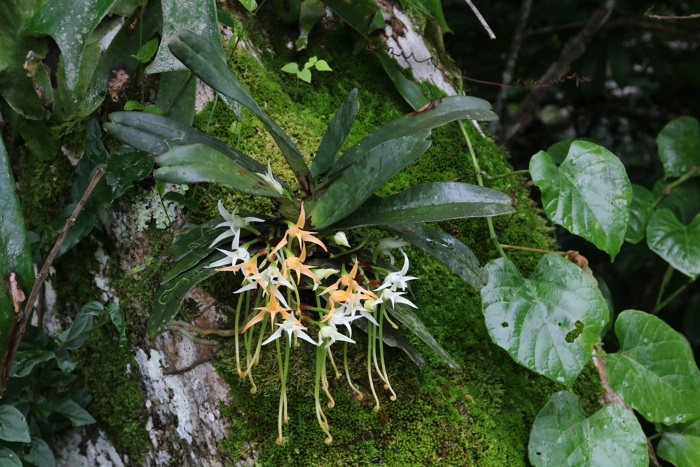
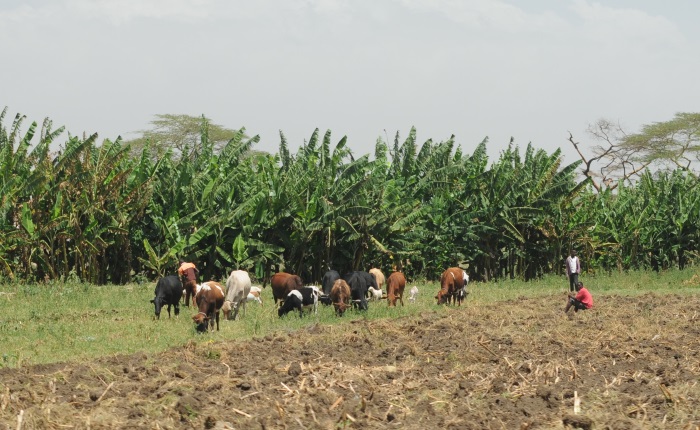
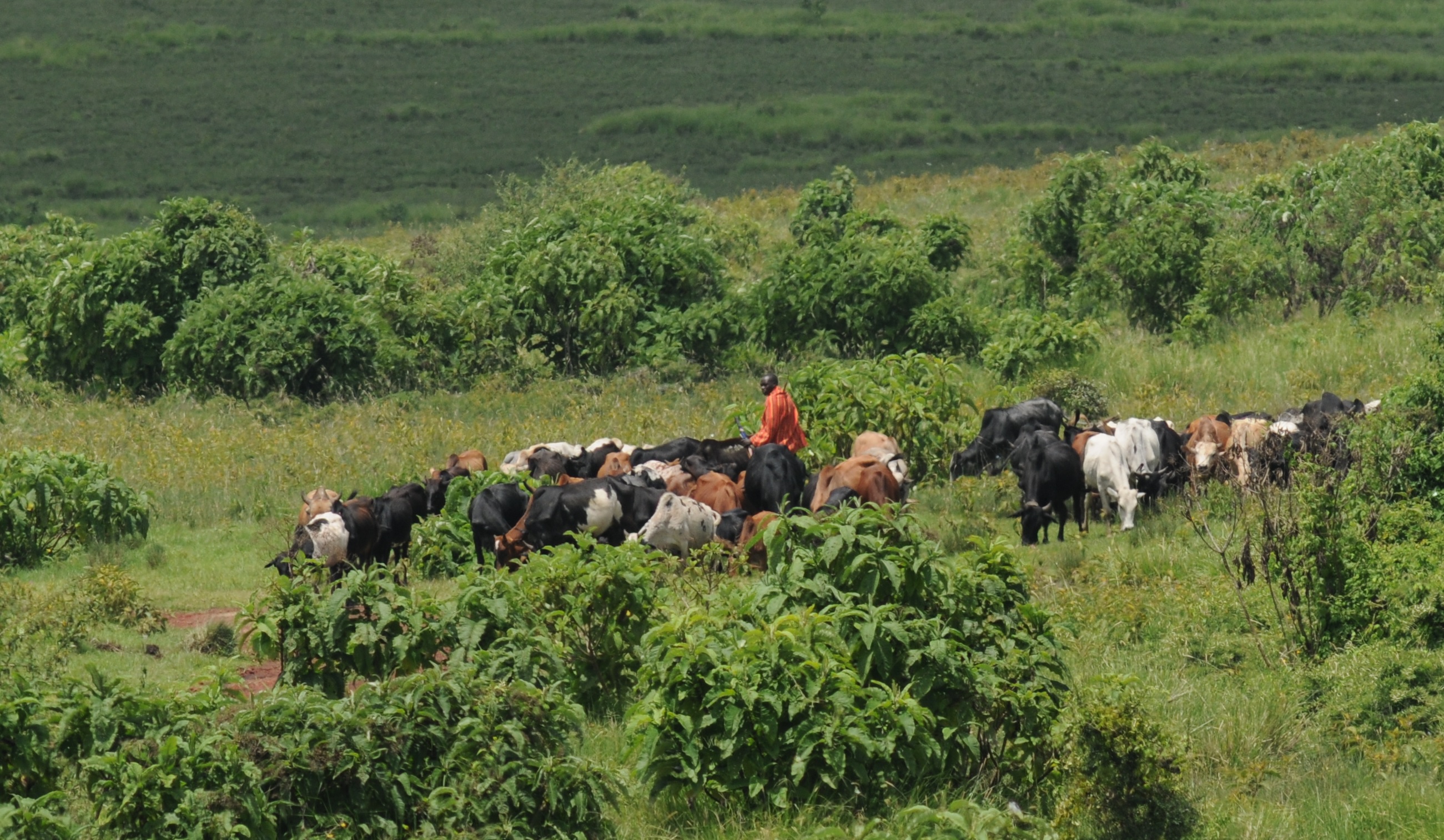
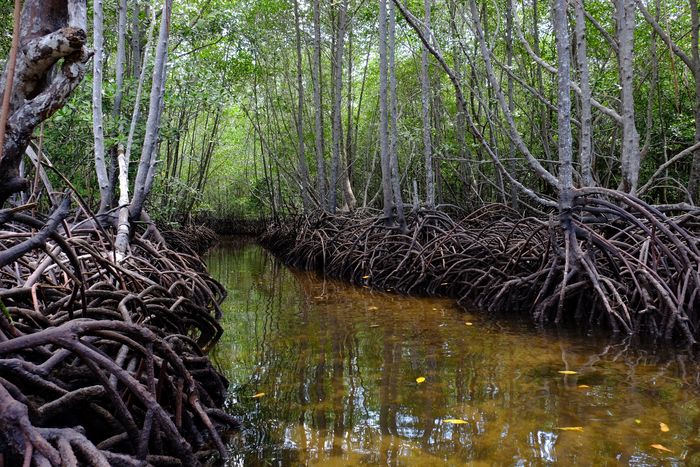
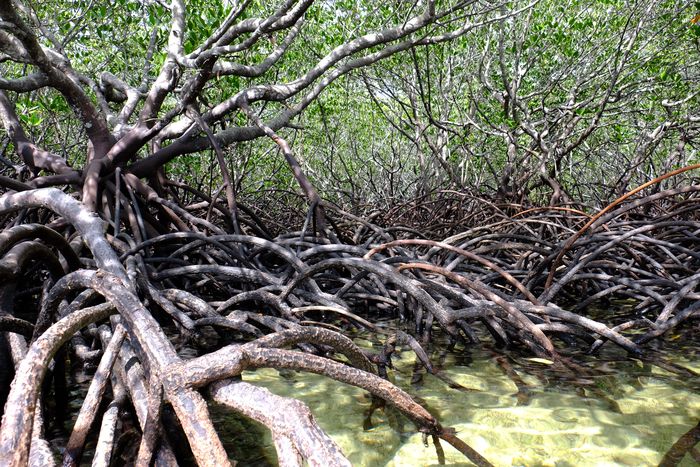
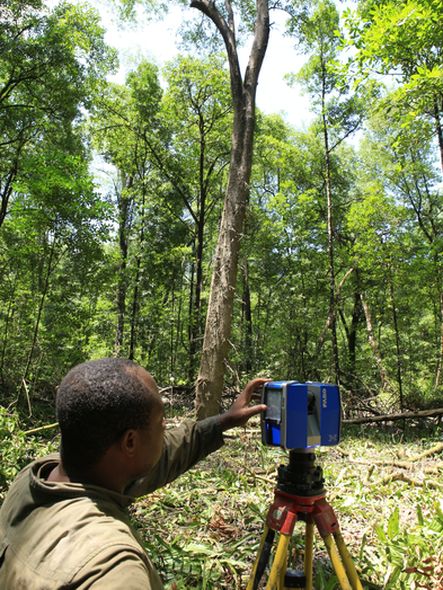
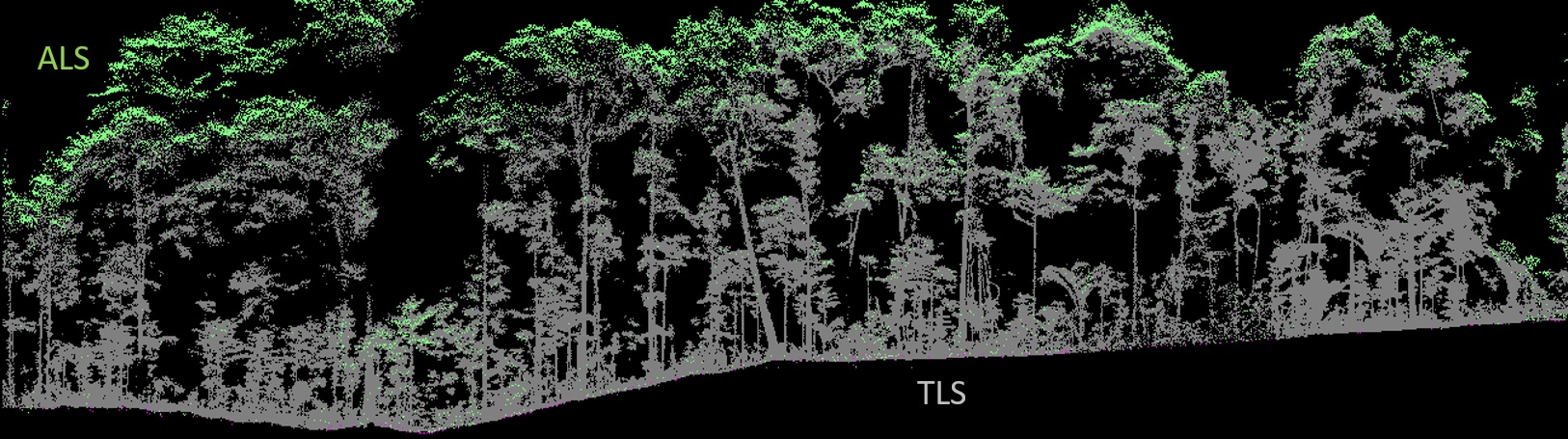
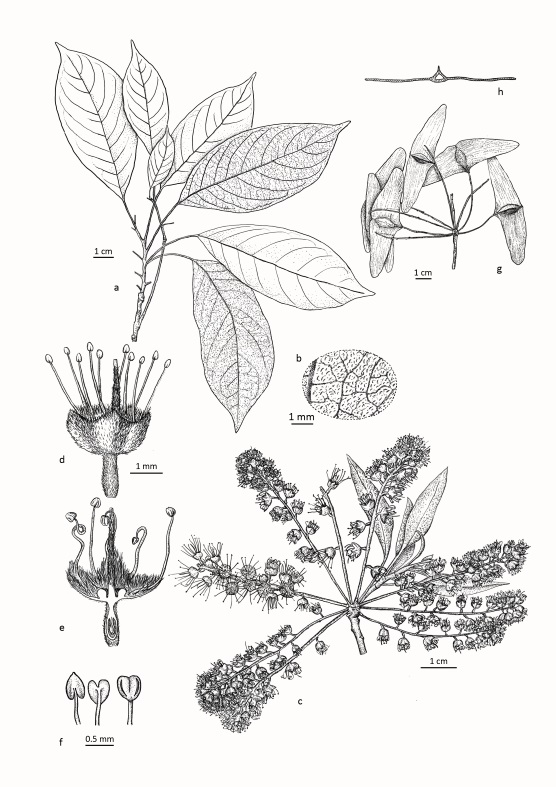
Our study sites are mainly in the North-West of the Mediterranean rim (Catalonia, France, Italy), South America (Brazil, Colombia, Bolivia, Peru, Argentina) and Central America (Mexico), Africa (South Africa, Cameroon, Ivory Coast, Kenya, Ghana), New Caledonia and the South-West Pacific area. We use of pre-existing data, perform field works and use online databases.
| Acronym | Title | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Biota Cerrado Network | Biota Cerrado Network Porteur : Guarino COLI (University of Brasilia) | 2024 - 2026 |
| DESSFOR | Degraded Stable States in Tropical Forests Porteur : Maxime REJOU-MECHAIN | 2021 - 2025 |
| FIRE-ADAPT | FIRE-ADAPT Porteur : Immaculada OLIVERAS MENOR | 2023 - 2026 |
| FLORAPYR 3D | Coopérer pour surveiller et conserver la flore pyrénéenne Porteur : Yann HELARY (CBNPMP) | 2024 - 2027 |
| LWI | Life Without Ice Porteurs : Olivier DANGLES (IRD, UR 072) / Sophie CAUVY-FRAUNIE (INRAE) | 2020 - 2026 |
| MELANOBS | Towards a Melanesian observatory of forest response to global change Porteur : Thomas IBANEZ | 2023 - 2025 |
| NATURAL FORESTORE | Capture and Storage of Carbon in Natural Tropical Forests Porteur : Emmanuel PARADIS (ISEM) | 2024 - 2027 |
| NeoFIRE | Understanding and scaling vulnerability of neotropical Amazon and transitional forests to altered fire regimes Porteur : Imma OLIVERAS (University of Oxford) | 2022 - 2026 |
| PLATWORM | Impact of the PLATyhelminthe Obama nungara invasion on earthWORM communities in France Porteur : Lise DUPONT (Université de Créteuil) | 2022 - 2025 |
| RaleGenets | Quel avenir pour le râle des genêts ? Exploration des scénarios possibles du socioécosystème des Basses Vallées Angevines Porteur : Cédric GAUCHEREL | 2024 - 2025 |
BIVAUD Lucie 2023 - 2026. Le réchauffement climatique souffle-t-il le chaud ou le froid sur les plantes de haute montagne ? Réduction du couvert neigeux, plantes nurses, et adaptations au froid en latitudes tempérées et tropicales. Ecole doctorale : GAIA / Université de Montpellier. Dir : ANTHELME Fabien
ROLAND RODRIGUES LIMA Héléna 2021 - 2025. Pendant son séjour à AMAP, elle sera supervisée par le Dr. Immaculada OLIVERAS MENOR (chercheuse IRD) et travaillera sur un projet intitulé "Fire in plant communities : understanding the abiotic and biotic drivers of flammability" (Feu dans les communauté. Ecole doctorale : Instituto de Pesquisas do Jardim Botanico do Rio de Janeiro / Instituto de Pesquisas do Jardim Botanico do Rio de Janeiro . Dir : OLIVERAS MENOR Immaculada
- South Africa : University of Cape Town; Witwatersrand University
- Germany: Bayreuth University; Idiv – Leipzig.
- Argentina : CONICET
- Australia: UniSA
- Bolivia: Herbario Nacional de Bolivia, Universidad Mayor San Andres
- Brazil: Universidade Estadual Paulista; UNEMAT; Universidade Estadual do Rio de Janeiro; INPE; CEMADEN
- Cameroon: Université de Yaoundé
- China: Chinese Academy of Sciences
- Colombia: Universidad de Los Andes ; Universidad Nacional de Colombia
- Spain: Fundacion Pau Costa; Universitat de Lleida ; University of Girona
- France: IMBE, univ. Aix-Marseille; CEFE – Montpellier; iEES Paris; ISEM – Montpellier, IGE - Grenoble.
- Netherlands : Utrecht University
- Italy: UniTo
- Kenya: Karatina University
- Mexico: CONAFOR; INECOL; UNAM
- New-Zealand : Landcare Research
- Peru: Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos, Universidad Nacional de Áncash Santiago Antúnez de Mayolo, Instituto de la Montaña, INAIGEM
- Poland: Mammal Reseach Institute, Bialowieza
- United-Kingdom : Kew Botanical Garden; Oxford University; University of Lancaster
- Sweden: Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences
- USA: Yale University